Conduktor Gateway on Kubernetes with SNI Routing
Step-by-step guide to deploying Conduktor Gateway on Kubernetes with host-based (SNI) routing, TLS certificates, and external Ingress access.

Video Walkthrough
Full tutorial walkthrough available above.
Why Host-Based Routing Matters
Conduktor Gateway is a Kafka protocol proxy with interceptor plugins for:
- Schema payload validation
- Business rule validation
- Field-level encryption and decryption
- Client configuration overrides
By default, Gateway uses port-based routing: each Gateway instance opens a port for each broker.
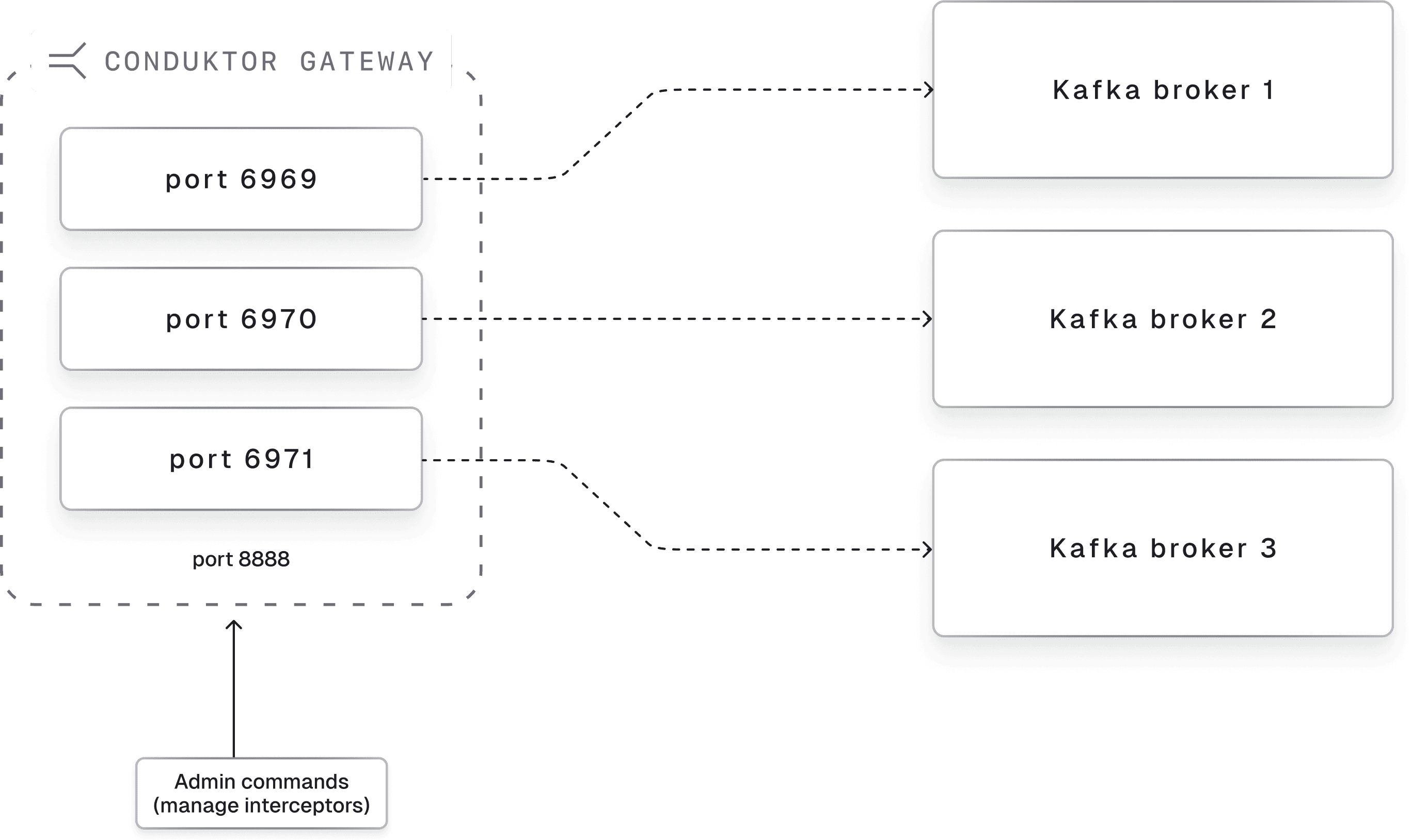
This breaks when broker counts change. Gateway exposes new ports automatically, but firewalls and load balancer targets need reconfiguration. With managed Kafka services, broker counts can change without warning.
Host-based routing (Server Name Indication, or SNI routing) solves this. Gateway exposes a single port and routes requests based on hostname instead of port. See the SNI routing guide for details.
This tutorial deploys SNI routing on Kubernetes with external client access via Ingress.
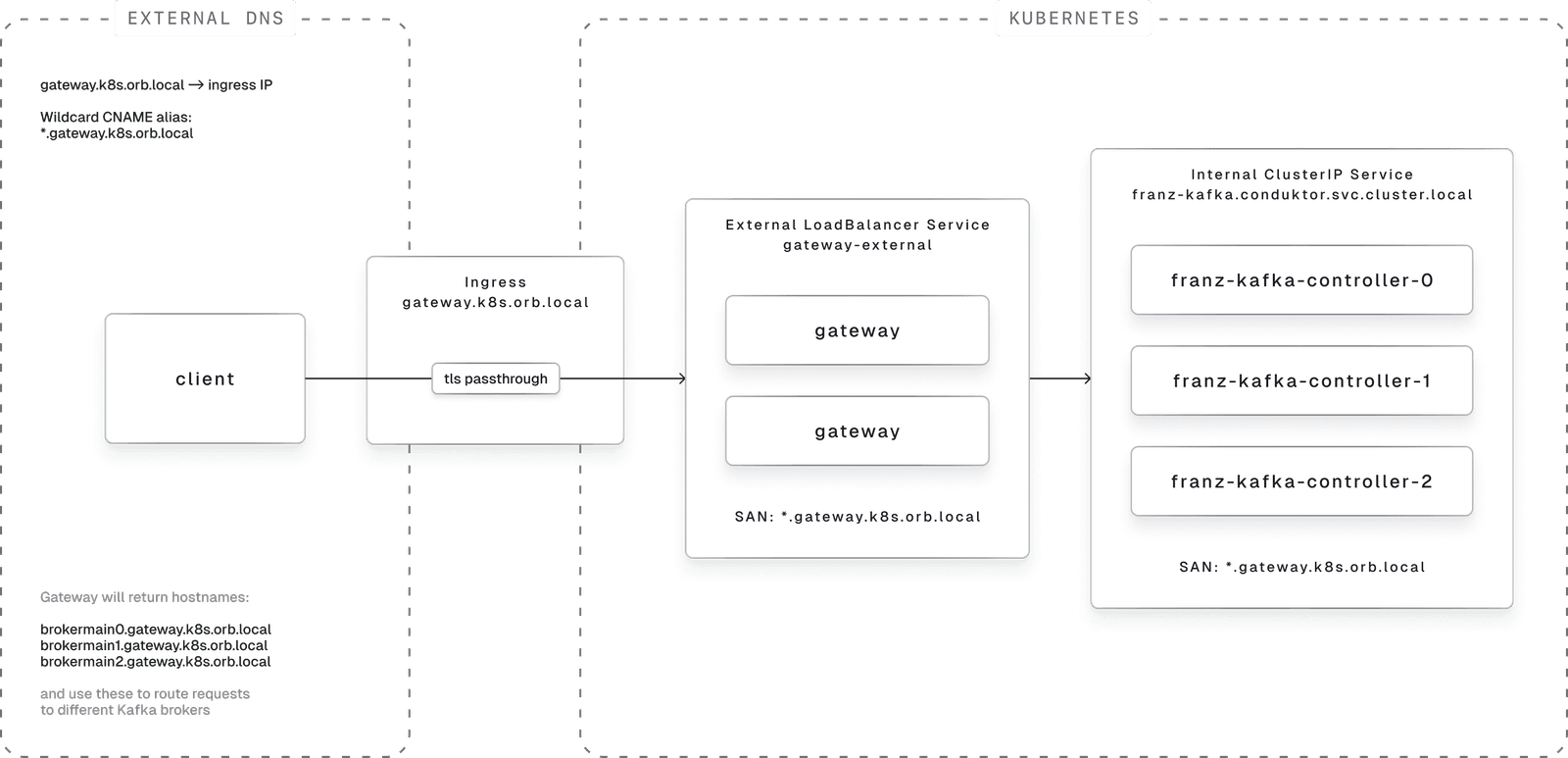
Architecture overview:
Prerequisites
This tutorial uses OrbStack (Mac only) for local Kubernetes. OrbStack's networking makes external Ingress access work locally without cloud resources or compromises.
Install dependencies:
brew install \
helm \
orbstack \
openssl \
openjdk \
kafka \
conduktor-cli- Helm: Kubernetes package manager
- OrbStack: Container and VM management with local Kubernetes
- OpenJDK: Required for
keytooland Kafka CLI tools
Add OpenJDK to your PATH in ~/.zshrc:
export PATH="/opt/homebrew/opt/openjdk/bin:$PATH"Generate TLS Certificates
TLS encrypts traffic between:
- Kafka clients and Conduktor Gateway
- Conduktor Gateway and Kafka
Generate keystores and truststore:
./generate-tls.shInspect the Gateway certificate:
openssl x509 -in ./certs/gateway-ca1-signed.crt -text -nooutThe Subject Alternate Names (SANs) are critical for SNI routing. Kafka clients need to reach specific brokers. Gateway impersonates brokers by presenting hostnames like brokermain0.gateway.k8s.orb.local for broker ID 0.
The client validates the certificate includes this hostname as a SAN. If missing, TLS handshake fails. Gateway then uses the SNI headers to route the request to the correct broker.
The wildcard * SAN handles broker additions without certificate, DNS, or infrastructure changes. When broker 4 appears, requests route automatically.
The generate-tls.sh script:
- Creates a certificate authority (CA)
- Creates the CA cert
- Signs service certificates for Kafka and Gateway
- Constructs wildcard SANs for broker impersonation
- Creates a truststore for client validation
Deploy Kafka and Gateway
./start.shThis script:
- Creates
conduktornamespace - Creates Kubernetes secrets for Kafka and Gateway
- Installs Kafka via Bitnami's Helm chart
- Installs Gateway via Conduktor's Helm chart
- Installs
ingress-nginxIngress Controller - Creates Ingress for Gateway
Review start.sh, the Helm values, and the Ingress definition for details.
Connect to Gateway
Test the admin API (no output means success):
export CDK_CACERT=certs/snakeoil-ca-1.crt
export CDK_GATEWAY_BASE_URL=https://gateway.k8s.orb.local:8888
export CDK_GATEWAY_USER=admin
export CDK_GATEWAY_PASSWORD=conduktor
conduktor get interceptorEquivalent REST API call (returns empty list on success):
curl \
--request GET \
--url 'https://gateway.k8s.orb.local:8888/gateway/v2/interceptor?global=false' \
--user "admin:conduktor" \
--cacert ./certs/snakeoil-ca-1.crtFor newer JDKs, set this environment variable (see KIP-1006):
export KAFKA_OPTS="-Djava.security.manager=allow"Add -Djavax.net.debug=ssl for SSL debug output.
Test Kafka Operations
Get metadata from Kafka directly:
kafka-broker-api-versions \
--bootstrap-server franz-kafka.conduktor.svc.cluster.local:9092 \
--command-config client.propertiesNote: OrbStack allows reaching internal services from your laptop. Normally this requires a pod inside the cluster.
Get metadata through Gateway (external access):
kafka-broker-api-versions \
--bootstrap-server gateway.k8s.orb.local:9092 \
--command-config client.propertiesNote: OrbStack routes *.k8s.orb.local to the Ingress Controller.
Create a topic through Gateway:
kafka-topics --bootstrap-server gateway.k8s.orb.local:9092 \
--create --topic test --partitions 6 \
--command-config client.propertiesList topics from Kafka directly:
kafka-topics --list \
--bootstrap-server franz-kafka.conduktor.svc.cluster.local:9092 \
--command-config client.propertiesList topics through Gateway:
kafka-topics --list \
--bootstrap-server gateway.k8s.orb.local:9092 \
--command-config client.propertiesProduce through Gateway:
echo "hello" | kafka-console-producer --topic test \
--bootstrap-server gateway.k8s.orb.local:9092 \
--producer.config client.propertiesConsume through Gateway:
kafka-console-consumer --topic test --from-beginning \
--bootstrap-server gateway.k8s.orb.local:9092 \
--consumer.config client.propertiesCleanup
Delete resources:
kubectl delete namespace conduktorOr use the convenience script:
./stop.shProduction Requirements
Your Ingress Controller must support layer 4 routing (TCP, not HTTP) with TLS passthrough.
- On AWS EKS: Use the Load Balancer Controller with Network Load Balancer (NLB)
- TLS passthrough lets Gateway read SNI headers during TLS handshake for broker routing
DNS requirements: Clients must resolve all Gateway-advertised hosts to the external load balancer. In this example, OrbStack routes *.k8s.orb.local to ingress-nginx, and our Ingress routes these hosts to gateway-external:
gateway.k8s.orb.localbrokermain0.gateway.k8s.orb.localbrokermain1.gateway.k8s.orb.localbrokermain2.gateway.k8s.orb.local
New brokers like brokermain3.gateway.k8s.orb.local route automatically.
Certificate requirements: Gateway's TLS certificate needs SANs for all broker hostnames. Wildcard SAN (*.gateway.k8s.orb.local) is simplest.
Load balancing: With external load balancers, Gateway's internal load balancing is unnecessary. The external load balancer distributes traffic.
Appendix: kcat Commands
Note: kcat has intermittent connection drops with OrbStack's ingress controller.
kcat -L -b franz-kafka.conduktor.svc.cluster.local:9092 \
-X security.protocol=SASL_SSL -X sasl.mechanism=PLAIN \
-X sasl.password=admin-secret -X sasl.username=admin \
-X ssl.ca.location=./certs/snakeoil-ca-1.crtkcat -L -b gateway.k8s.orb.local:9092 \
-X security.protocol=SASL_SSL -X sasl.mechanism=PLAIN \
-X sasl.password=admin-secret -X sasl.username=admin \
-X ssl.ca.location=./certs/snakeoil-ca-1.crtecho "hello1" | kcat -t test -P -b gateway.k8s.orb.local:9092 \
-X security.protocol=SASL_SSL -X sasl.mechanism=PLAIN \
-X sasl.password=admin-secret -X sasl.username=admin \
-X ssl.ca.location=./certs/snakeoil-ca-1.crtkcat -t test -C -b gateway.k8s.orb.local:9092 \
-X security.protocol=SASL_SSL -X sasl.mechanism=PLAIN \
-X sasl.password=admin-secret -X sasl.username=admin \
-X ssl.ca.location=./certs/snakeoil-ca-1.crt